
This is very useful to choose which extra features do we want into the Kernel and which drivers will be included in the monolithic Image or supplied as external modules.Īs we do not need to perform any customization in our examples, we can just Exit the interface. If we need to perform some customization in the Linux Kernel image, we can access to the ncurses based graphical configuration menu: make menuconfigĪfter doing this, the terminal will become a (quite) friendly graphical interface for the Linux Kernel configuration: The reason is that, in opposition to the U-Boot case, the Kernel configuration is totally generic for a given MPSoC family and the Device Tree is in charge of further System-on-Chip or board level customizations.įor this reason, in order to configure the Linux Kernel with the generic features to support a Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC based platform, we just need to execute this command: make xilinx_zynqmp_defconfig
#Linux kernel modules install
For Debian/Ubuntu Debian distributions, these packages can be installed via the package manager with these commands: sudo apt-get install build-essential sudo apt-get install flex sudo apt-get install bison sudo apt-get install libncurses-dev sudo apt-get install libssl-dev Setting the Environment Required Host Packagesīefore performing the exercises, some packages need to be installed in the development host Linux Operating System.

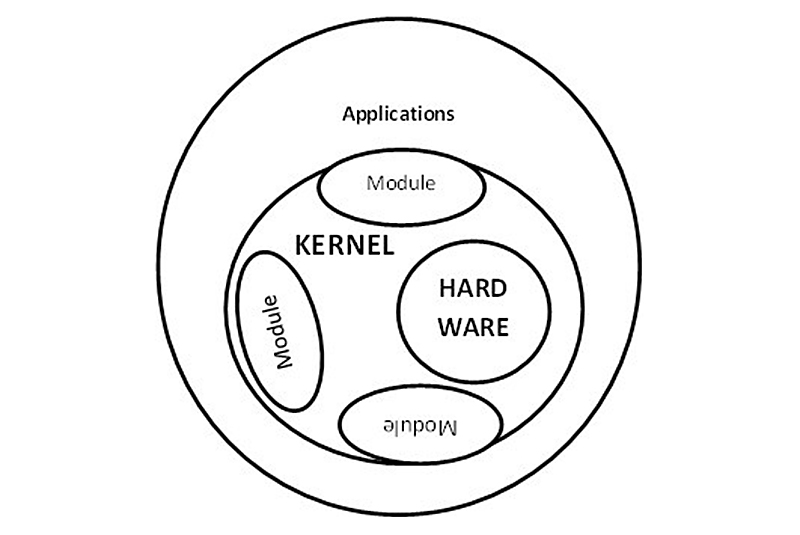
In this section, we will build the Linux Kernel components for booting a complete Linux based runtime in the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC. An optional set of external Linux Kernel Modules that are located in the root filesystem and loaded only when needed.A monolithic Linux Kernel Image that contains the main functionality and drivers that must be loaded at any time.The Linux Kernel is the core component of a Linux based runtime and provides multiple functionalities:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
